Supplemental: Using Git from VSCode
Overview
Teaching: 10 min
Exercises: 0 minQuestions
How can I use Git with VSCode?
Objectives
Understand how to use Git from VSCode.
Visual Studio Code (VSCode, not to be confused with “Visual Studio”) is a powerful and full featured Interactive Development Environment (IDE). It is language agnostic, and has many excellent features right out of the box, as well as a large number of extensions that can be installed easily from within the app itself. Even die-hard Microsoft Avoiders love VSCode!
Since version control is recommended best practice for any research, writing, or analysis work that you are doing many IDEs have git integrations, and VSCode is no different.
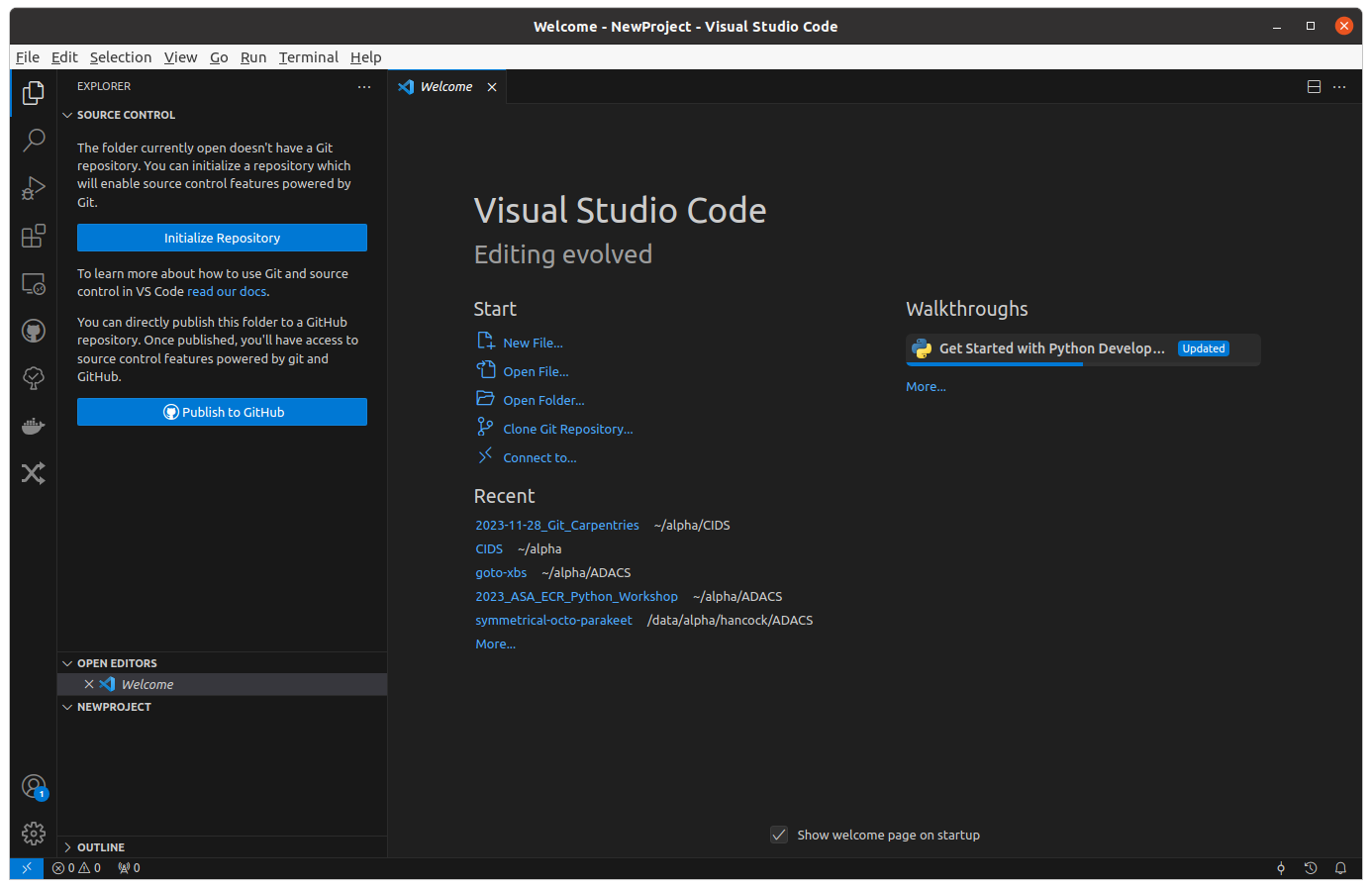
If we create a new workspace in VSCode, the default view will prompt us to create a git repo before we event create any files!
To make a new git repo (equivalent of git init) just press the “Initialize Repository” button shown below.
Once you have a local git repo you can connect your repo to github by pressing the “Publish Branch” button which will let you choose a repo name:
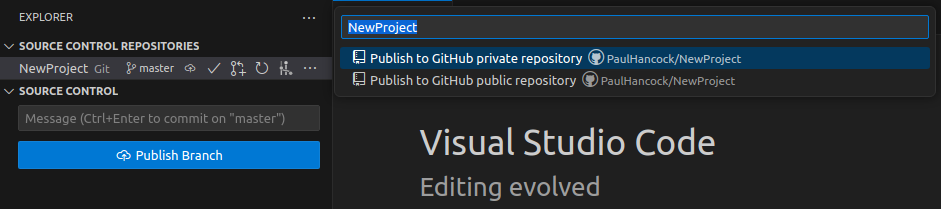
From here you can use the current directory name as the project name or choose your own (or an existing, empty repo).
The left panel will show you the following collapsible sections:
- Source control repositories
- In case this directory tree has multiple repos, you can select them here
- Source control
- For the current repository you can see which files have changed with a symbol showing the file status
- Open editors
- A list of all the tabs you have open
- A file explorer
- For exploring your project, creating files/directories, and opening files.
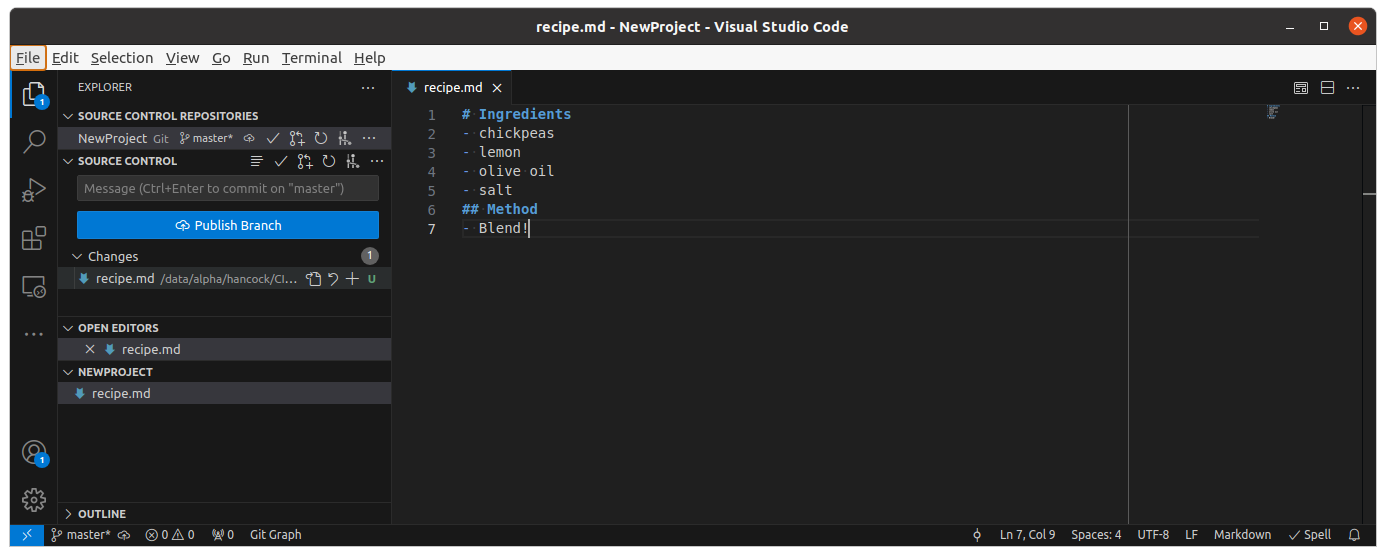
Using the Source Control panel can be done as follows:
- Edit and save a file
- The file appears in the “Changes” list.
- Hover over the file and you’ll see three icons: open file, discard changes, stage changes (+).
- Click on the stage changes (+) button and the file will move to a new list called “Staged Changes”
- The file now has two icons: open file, and unstage changes (-)
- Click on the file to see the changes in a view that is nicer than the default
git diff - From this side-by side view you can even select some changes to not commit using the “Unstage Selected Ranges” option from the right click menu.
- When you have staged changes to commit you type a message into the “Message” box and press the “Commit” button.
- The button will now change to either “Publish Branch” if there is no connected remote, or to “Push” if you have a remote.
Push a commit to your repo
- Using VSCode navigate to “File -> Open Folder” and open your current project
- Select a file to change from the file explorer
- Make a small change to the file, save it, and then stage and commit that change using the source control panel.
Branching
The bottom left of your VSCode window will have a note to tell you the current branch you are on. Click this name and select a different branch to work on, or enter a name to create a new branch.
Manual git commands via the terminal
VSCode has a built in terminal that you can access via Ctrl+`.
From here you can run any git command you like and it wont mess with what VSCode is doing.
You can hide the terminal again by pressing Ctrl+` again.
Resolving merge conflicts
If you encounter a dreaded merge-conflict then VSCode can make your life a lot easier.
The default view will highlight conflicts for you and label then so that you know what the >> and << sections correspond to.
You’ll also get some nifty short cuts for accepting either or both changes.
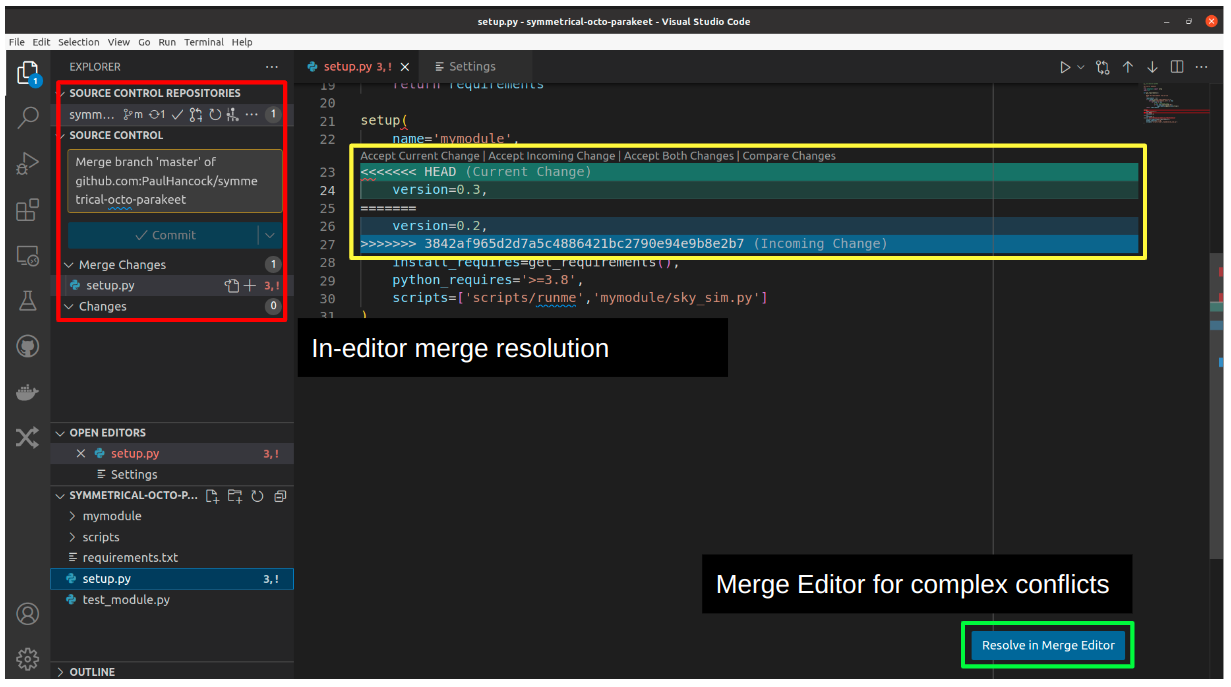
For more complex merge conflict resolution you chan use the “Merge Editor” which gives you a three panel view:
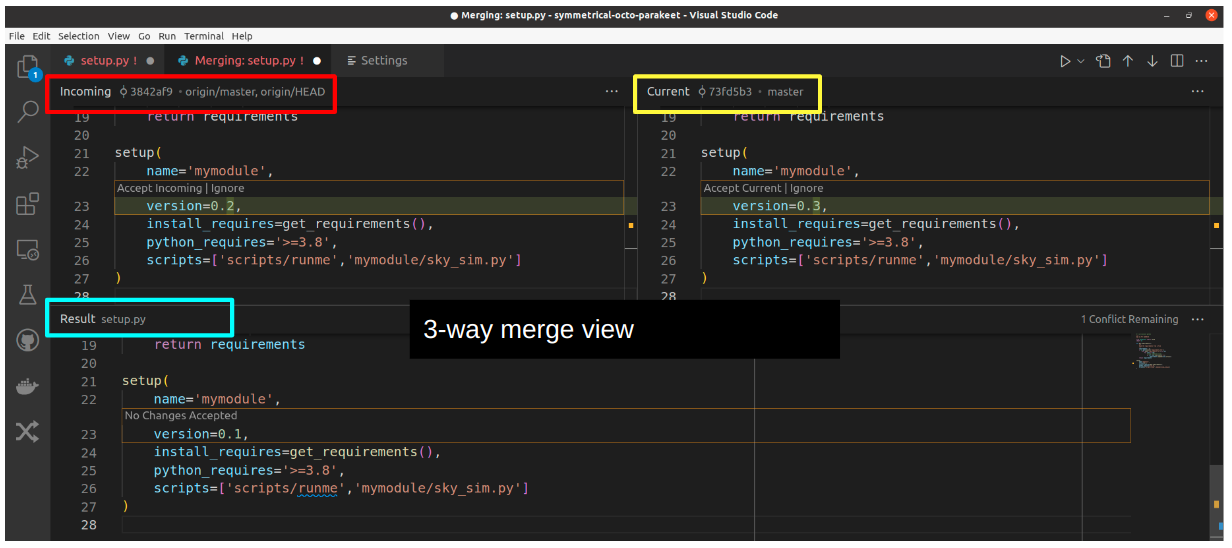
Even more
Using an extension you can:
- view/create issues and pull requests on GitHub via VSCode
- manage docker containers
- run all the tests for your code (which you have a lot of right?)
- debug your code with an interactive debugging environment
- open, edit, and even execute code on a remote server
Explore the extension tab to see more.
Key Points
Using VSCode’s Git integration allows you to forget all the git command syntax and focus on work.